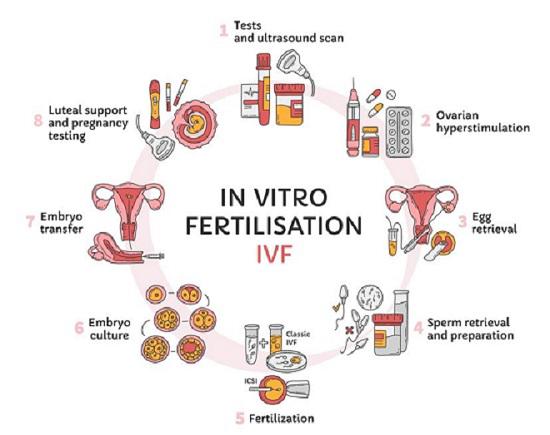
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex medical procedure aimed at assisting individuals or couples struggling with infertility. It involves fertilizing an egg outside the body, in a laboratory setting, before implanting the embryo into the uterus. This advanced fertility treatment has helped many families conceive when other methods were unsuccessful.
Knowing How IVF Procedure
The IVF procedure begins with ovarian stimulation. In this phase, fertility medications are prescribed to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This is crucial because, in a natural cycle, only one egg is typically released. By stimulating the ovaries, doctors increase the chances of retrieving several eggs, improving the odds of successful fertilization.
Once the eggs are mature, they are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure known as egg retrieval or aspiration. During this step, a thin needle is inserted into the ovaries, guided by ultrasound, to extract the eggs. This procedure is usually performed under mild sedation to minimize discomfort.
Meanwhile, a sperm sample is collected from the male partner or a donor. The sperm is then prepared in the laboratory, where the healthiest and most motile sperm are selected for fertilization. If male infertility is an issue, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be employed. In ICSI, a single sperm is directly injected into an egg, enhancing the chances of fertilization.
The next step is fertilization itself. The selected eggs and sperm are combined in a laboratory dish, where they are left to incubate for several days. During this time, the sperm will ideally penetrate and fertilize the eggs, leading to the development of embryos. These embryos are monitored closely by embryologists to assess their growth and development.
Once the embryos reach a certain stage, typically on day five or six, the healthiest embryo(s) are selected for transfer into the woman’s uterus. The embryo transfer is a relatively simple procedure performed without anesthesia. A thin catheter is used to place the embryo directly into the uterus. In some cases, multiple embryos may be transferred to increase the chances of implantation.
After the transfer, the waiting period begins. About 10 to 14 days later, a pregnancy test is performed to determine if the embryo has successfully implanted into the uterine lining. If the test is positive, the pregnancy proceeds just like a natural conception. If the test is negative, the couple may need to repeat the IVF cycle or explore other options.
It is important to note that IVF success rates vary depending on factors such as the woman’s age, the quality of the eggs and sperm, and the specific fertility challenges the couple faces. Some individuals may require multiple IVF cycles before achieving a successful pregnancy.
IVF is a significant medical advancement that has offered hope to many individuals struggling with infertility. However, it can also be emotionally and physically demanding. The process involves a series of hormonal treatments, medical procedures, and a degree of uncertainty, as success is not guaranteed with every cycle.
Despite these challenges, many couples find IVF to be a worthwhile option when faced with infertility. By working closely with fertility specialists, patients can receive personalized care and guidance throughout the process, helping to improve their chances of success. For those who are unable to conceive naturally, IVF provides a pathway to parenthood that might not have been possible through traditional methods.