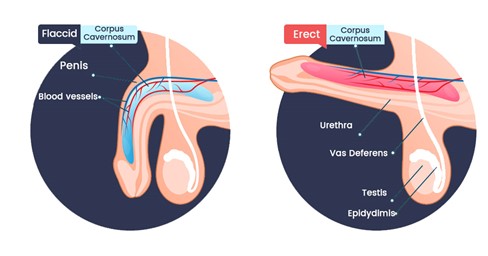
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that many men experience at some point. Occasional difficulties with erections are normal, but if the issue persists, it may be time to seek medical attention. Often, erectile dysfunction is linked to underlying health conditions, and addressing those issues can sometimes reverse the problem. When necessary, medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and therapy are available.
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. It can be classified into two types:
Primary Erectile Dysfunction: A rare condition where a man has never been able to have or sustain an erection.
Secondary Erectile Dysfunction: A more common form that occurs in men who previously had normal erectile function.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
ED can stem from various physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Some of the key causes include:
Physical Causes: Conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, hormonal imbalances, and chronic kidney disease can affect blood flow or nerve function, leading to ED.
Psychological Causes: Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship issues can all contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of exercise, and poor diet can increase the likelihood of ED.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
Common symptoms of erectile dysfunction include:
Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
Reduced sexual desire
Diagnosing Erectile Dysfunction
Doctors diagnose ED by assessing your medical history, performing physical examinations, and ordering diagnostic tests. Some of these evaluations include:
Medical History: A review of any health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or previous pelvic surgeries that may contribute to ED.
Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the penis, testicles, and nerves to check for physical abnormalities.
Blood and Urine Tests: These can identify underlying health conditions like diabetes, hormonal imbalances, or cardiovascular issues.
Ultrasound: A specialist uses a transducer to examine blood flow to the penis. Sometimes, medication is injected into the penis to stimulate an erection for further evaluation.
Psychological Examination: Screening for mental health issues such as stress, anxiety, or depression that may be contributing to ED.
Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can be treated through a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and other therapies.
Lifestyle Changes:
Exercise: Engaging in moderate to vigorous aerobic activity improves blood flow, reduces stress, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Diet: A Mediterranean-style diet rich in whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and healthy fats can help improve sexual function.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to ED. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake can improve erectile function.
Medications:
Oral Medications: Drugs such as sildenafil (Viagra) enhance the effects of nitric oxide, a natural chemical in the body that helps relax the muscles in the penis, increasing blood flow and enabling erections.
Hormone Therapy: For men with low testosterone levels, hormone replacement therapy can be effective, either as a standalone treatment or combined with other therapies.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing erectile dysfunction, don’t hesitate to consult a medical professional. Addressing underlying health conditions, making lifestyle changes, or seeking appropriate treatments can help restore normal sexual function. Clinics like Oasis Fertility provide advanced solutions and expert care for reproductive health issues, offering cutting-edge treatments and assistive reproductive technologies like IVF to help couples achieve their goals.