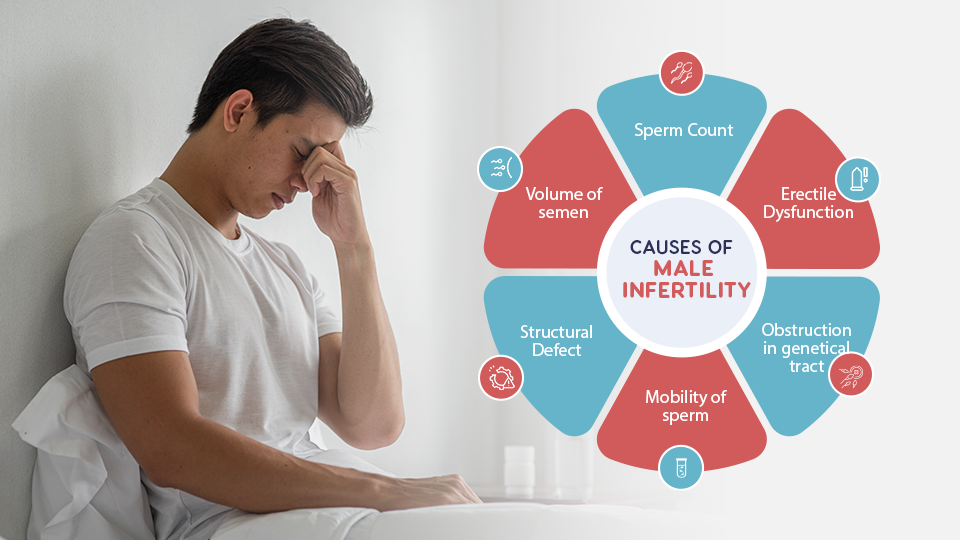
As men age, their fertility can decline, leading to increased concerns about male infertility. Unlike women, who experience a clear reproductive decline with menopause, men can remain fertile into their later years. However, age can significantly affect various aspects of male reproductive health.
Sperm Quality and Quantity
One of the primary ways age impacts male fertility is through the decline in sperm quality and quantity. Research shows that men over 40 often experience decreased sperm motility, morphology (shape), and overall count. A study published in Fertility and Sterility found that men aged 40 and older produced sperm with lower motility and higher DNA fragmentation than their younger counterparts. This decline can make it more difficult for sperm to fertilize an egg, increasing the time it takes to conceive or leading to infertility.
Hormonal Changes
Aging also brings hormonal changes that can contribute to infertility. Testosterone levels typically decline as men age, which can impact libido and sexual function. Lower testosterone can lead to reduced sperm production, resulting in fewer viable sperm available for fertilization. Moreover, hormonal imbalances may affect the production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which play crucial roles in sperm production and regulation.
Increased Risk of Genetic Abnormalities
Older age in men is associated with a higher risk of genetic abnormalities in sperm. As men age, the DNA in their sperm may become damaged or mutated, which can lead to developmental issues in offspring, including congenital disabilities. Studies have indicated that children born to older fathers have a slightly higher risk of conditions such as autism and schizophrenia. This risk may be attributed to the accumulation of mutations over time and reduced DNA repair mechanisms in older men.
Associated Health Conditions
Another factor contributing to male infertility with age is the increased likelihood of health issues, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. These conditions can negatively impact sperm production and function. For instance, obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances that reduce testosterone levels, further affecting fertility. Additionally, chronic health conditions may necessitate medication that could have adverse effects on sperm health.
Psychological Factors
Psychological aspects of aging can also play a role in male infertility. Older men may experience increased stress or anxiety regarding their fertility and parenthood, which can further complicate conception efforts. Emotional well-being is crucial for sexual function and reproductive health, making it essential for older men to address any psychological barriers they may face.
Conclusion
While age is an important factor in male fertility, it is not the sole determinant. Many men over 40 can still conceive successfully, especially with lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and a healthy approach to reproductive health. Men experiencing fertility issues should consult healthcare professionals for appropriate evaluation and treatment options. By understanding the impacts of age on male fertility, men can make informed choices about family planning and seek assistance if needed.