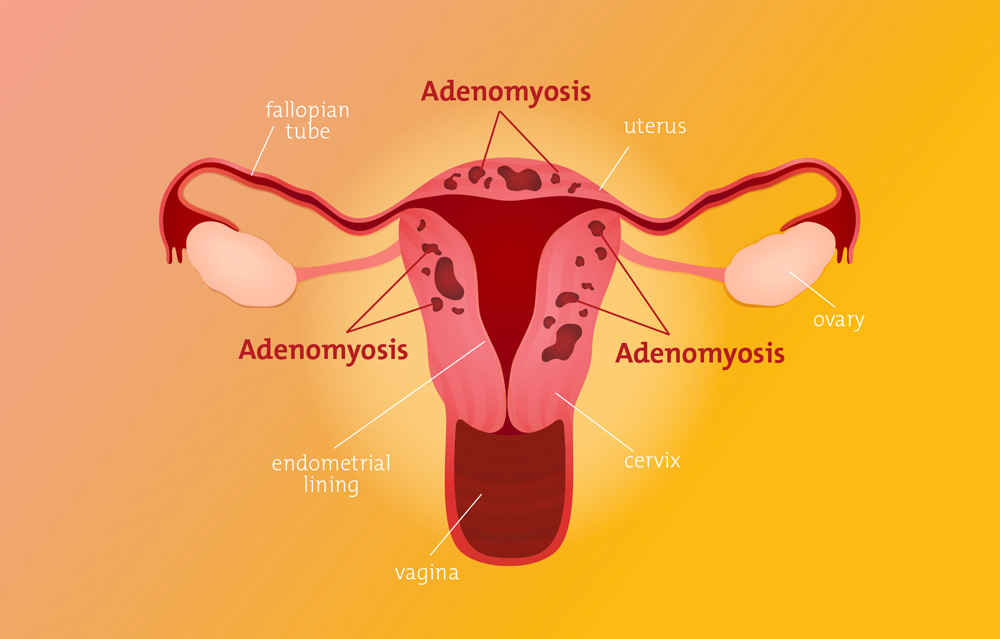
Adenomyosis is a condition affecting women in which the inner lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium, grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, or myometrium. This benign condition can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, significantly impacting a woman’s quality of life. Understanding adenomyosis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of adenomyosis remains unclear, but several theories exist. One possibility is that it results from the implantation of endometrial tissue into the uterine muscle during the menstrual cycle. Hormonal influences, particularly estrogen, may also play a role in its development. Risk factors include:
Age: Adenomyosis is most commonly diagnosed in women aged 30 to 50.
Childbirth: Women who have had multiple pregnancies are more likely to develop the condition.
Previous uterine surgery: Surgical procedures, such as a cesarean section or fibroid removal, can increase the risk.
Symptoms
Adenomyosis can present with various symptoms, which can vary in severity from woman to woman. Common symptoms include:
Pelvic pain: This is often described as a dull ache and may be more intense during menstruation.
Heavy menstrual bleeding: Many women experience heavier than normal periods (menorrhagia).
Prolonged menstrual bleeding: Some may notice their periods last longer than usual.
Pain during intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sexual activity is also reported.
Other symptoms: Fatigue, bloating, and pressure symptoms in the lower abdomen can occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing adenomyosis can be challenging, as its symptoms often overlap with other conditions, such as fibroids or endometriosis. A healthcare provider may use several methods to diagnose adenomyosis, including:
Pelvic examination: A physical exam may reveal an enlarged uterus.
Imaging tests: Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are the most effective tools for visualizing adenomyosis.
Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to rule out other uterine conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for adenomyosis is tailored to the individual, based on symptom severity, age, and reproductive goals. Options include:
Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort.
Hormonal therapies: Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or other hormonal treatments can help regulate menstrual bleeding and reduce pain.
Surgery: In severe cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be considered, particularly for women who do not wish to conceive in the future.
Alternative therapies: Some women find relief through dietary changes, acupuncture, or stress management techniques.
Conclusion
Adenomyosis is a significant gynecological condition that can lead to considerable discomfort and lifestyle challenges. With a better understanding of the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, women can seek timely medical advice and find the appropriate management strategies. If you suspect you have adenomyosis or experience concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and support. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.